News
Preservation project of the Upper Anubis Shrine
Until 2002 the vault of the Anubis Shrine was protected by a temporary wooden shelter in the form of a gable roof with a slope of ~45°. The latter were supported on one side on the top of the north wall of the Solar Court and on the other on the heavily eroded rock slope.
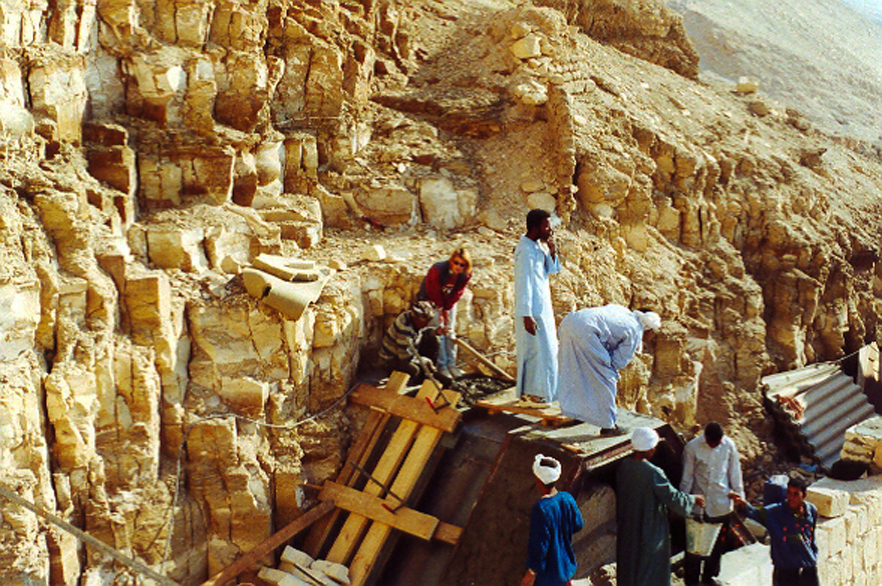
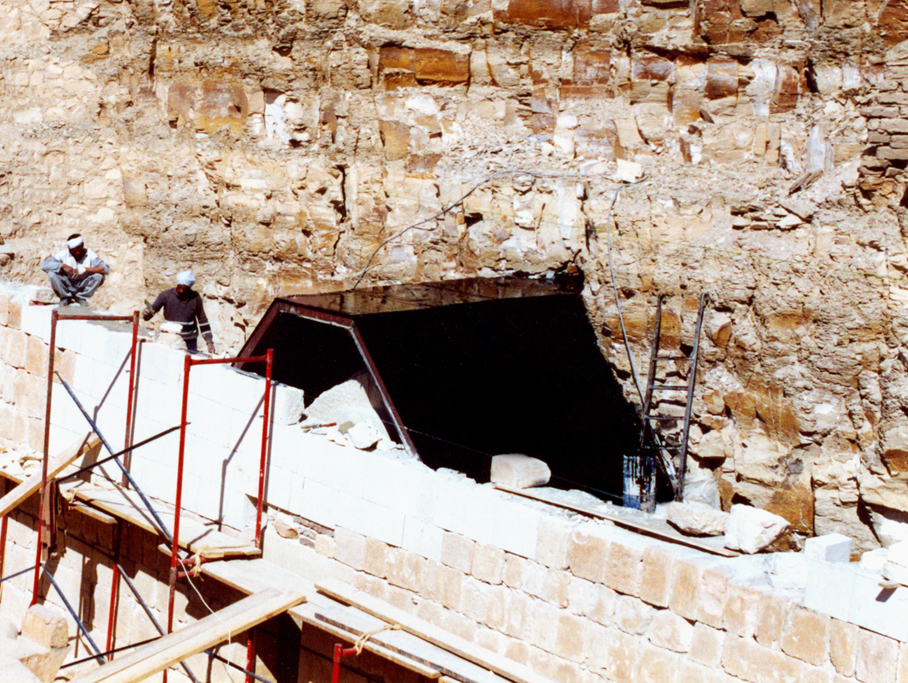
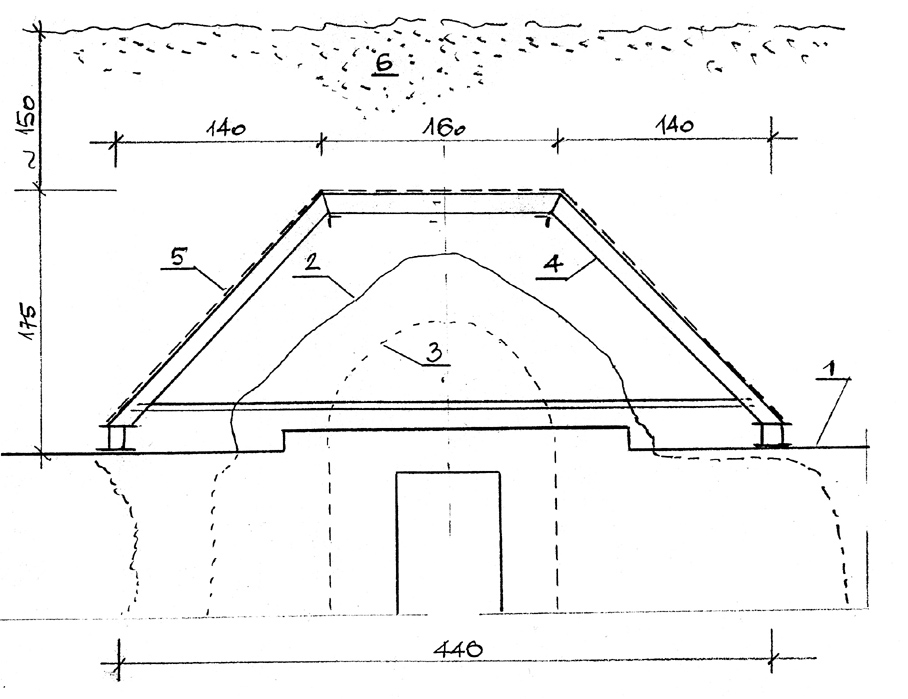 The technical condition of this shelter structure left much to be desired with the outer roofing damaged, frayed at the roof edges and with sections missing.
The technical condition of this shelter structure left much to be desired with the outer roofing damaged, frayed at the roof edges and with sections missing.
It no longer served its purpose. Design guidelines for protecting the shrine and installing a roof above it were prepared by Mieczysław Michiewicz previously in 1999.
The technical design for the roof satisfied the following physico-technical functions:
1. protection from rainfall and water flow from neighboring rock slope;
2. protection from dynamic rock fall from considerable heights and uncontrolled burial under rock detritus from the neighboring rock slope;
3. safe transfer of the load of rock detritus from the planned burial of the shelter roof up to 1.50 m high;
4. ensuring ventilation of space between the top of the shrine vault and the shelter roof
5. protection from temperature variation, water condensation and ultraviolet radiation.


Bibliography:
Project participants: Teresa (Kaczor) Dziedzic, Mieczysław Michiewicz
Contact: teresa.dziedzic@pwr.wroc.pl
Egyptological projects I Archaeological projects I Conservation and architectural projects I Field reports I History of research